HTML clipboardINTRODUCTION: Futures trading started way back in 1865 on the Chicago Board of Trade (CBOT), but prior to 1972, the underlying asset of futures contracts were agricultural commodities. The futures market met the needs of farmers and merchants. It overcame a few of the drawbacks related to the forwards market (Refer Exhibit I) like non-standardization of contract and credit risk.
Trading in financial futures started only after the World War II on the two largest exchanges i.e. the CBOT and the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME). Post-1972, there was further development of futures contracts, with the introduction of a range of financial instruments. However, it was only in 1994, that these financial products started to be traded electronically. DEFINING THE TERMS: A futures contract is an agreement between two parties to buy or sell an asset at a certain time in the future at a certain price. The underlying asset of a futures contract may be an agricultural commodity (such as corn, wheat, soybean, or soybean oils), or a financial instrument (such as treasury bonds, treasury notes and shares). Unlike forward contracts , futures contracts are standardized (in terms of contract size, expiration month, trading cycle, etc.) and are traded in an organized exchange. In referring to futures contracts, there are number of other terms that are commonly used. Spot price is the price at which an asset trades in the spot market .
The price at which the futures contract trades in the futures market is called the futures price (Refer Exhibit II). A contract cycle is the period over which a contract trades. An investor can take two positions in a futures contract, a 'long futures position'or a 'short futures position.'The investor is said to have taken a long position when he/she is buying, and is said to have taken a short position when he/she is selling, a futures contract. Expiry date is the last day on which the contract is traded at the end of which it will cease to exist. The amount of the asset that has to be delivered under a contract is known as the contract size. The difference between two futures prices is known as spread. The difference between two futures prices for the same underlying commodity on two different expiration dates is known as 'intra commodity'spread. The difference between two futures prices for two different but related commodities is known as 'inter commodity'spread. The price difference between the two markets for the same commodity is known as 'inter market'spread.
In the context of financial asset futures, basis is defined as the futures price minus the spot price. In a normal market , the basis is positive, reflecting the fact that futures prices normally exceed spot prices. However, in case, the futures prices are less than the spot prices, the difference is known as backwardation. Another definition of basis is the difference between spot price of the asset to be hedged and the futures price of the contract of that asset. Cost of carry shows the relationship between future prices and spot prices. It measures the storage cost plus the interest paid minus the income earned.
The members who execute the trades on the exchange floor are floor brokers and floor traders. The brokers who execute the order on others'account are known as floor brokers. They act according to the wishes of their customers and are basically agents for public investors. Floor traders execute trades exclusively on their own account. Those floor traders who also execute trades on others account are known as dual traders, and the mechanism is known as dual trading. In the market, some of the floor traders are known as scalpers. They are the individuals who trade on their own account and stand ready either to buy or sell. They are also called as locals and by their active participation provide liquidity to the futures market. DEFINING THE TERMS Contd.. The participants in the market are classified as hedgers, speculators and arbitrageurs. Hedgers use futures market to reduce or eliminate the risk associated with price fluctuations of an asset. For example, an exporter whose receivables are denominated in another currency (say, Euro) runs a significant foreign exchange risk, because of the possible adverse movement in the price of the other currency vis-a-vis the home currency. The exporter can hedge the above risk by selling futures in Euro. Speculators are those who are willing to take the risk that the hedgers are seeking to avoid. They use futures contracts to benefit from betting on future movements in the price of an asset. They seek to make gains by taking long and short positions in futures based on their own views and forecasts about the market. Arbitrageurs look for profit from the discrepancy between prices in two different markets. CLEARING HOUSE: A clearing house is a part of the futures exchange and acts as an intermediary in futures transactions. All futures contracts are routed through a clearing house which is a 'de facto'guarantor for all futures transactions. A clearing house works closely with the exchange but is an entity distinct from the exchange. Since all transactions are routed through it, the clearing house becomes the buyer to every seller and seller to every buyer. Let us understand the process with the help of following illustration:
There are two parties, A and B, who want to enter into a futures contract. A typical transaction with, and without, the involvement of a clearing house would be as follows: In the first case, where the transaction takes place without the clearing house both A and B assume the counterparty risk because on the date of the contract, B may fail to deliver the underlying asset or A may fail to pay the price. In the second case, the clearing house replaces B as a seller to A, and A as a buyer to B, and thus the credit risk taken by both A and B becomes insignificant. FIGURE I
TRANSACTION WITHOUT CLEARING HOUSE 
TRANSACTION INVOLVING CLEARING HOUSE
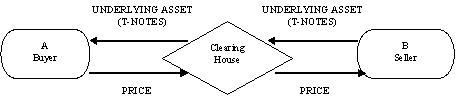 The clearing house assumes many important functions like ensuring smooth trading by maintaining delivery schedules, minimizing credit risk by becoming counterparty to every transaction, monitoring speculation margins and more. Since the clearing house undertakes counterparty risk for all transactions, the total risk assumed by it is high. Thus, it becomes important for the clearing house to minimize this risk, which is done by collecting margins. Margins are levied for all transactions depending on the volatility of the underlying asset, and adjustment is done everyday depending upon the prices, a process known as marking to market. |